CRM Software Cost: Understanding Pricing Models And Hidden Expenses
When it comes to CRM software cost, navigating through pricing models and hidden expenses can be a daunting task for businesses. Let’s delve into the intricacies of what influences these costs and how businesses can budget effectively.
Overview of CRM Software Costs
When considering CRM software costs, it is essential to understand the various types of expenses associated with implementing and maintaining such systems. From initial setup fees to ongoing subscription costs, businesses need to factor in several elements when budgeting for CRM software.
Types of Costs Associated with CRM Software
- Initial Setup Fees: These costs cover the implementation and customization of the CRM software to suit the specific needs of the business.
- Subscription Fees: Many CRM software providers offer subscription-based pricing models, where businesses pay a monthly or annual fee to access the software.
- Training and Support Costs: Businesses may incur additional expenses for training employees on how to use the CRM software effectively, as well as for ongoing technical support.
- Integration Costs: Integrating CRM software with existing systems and applications can involve additional expenses, such as hiring developers or purchasing integration tools.
- Upgrade and Maintenance Costs: Over time, businesses may need to invest in upgrades and maintenance to ensure their CRM software remains up-to-date and functional.
Factors Influencing CRM Software Pricing
- Features and Functionality: The more advanced features and customization options a CRM software offers, the higher the cost is likely to be.
- Number of Users: Pricing for CRM software may be based on the number of users who will be accessing the system, with larger user bases typically resulting in higher costs.
- Deployment Model: Whether a business opts for on-premise or cloud-based CRM software can impact pricing, as cloud solutions often involve subscription fees.
- Vendor Reputation: Established CRM software vendors with a strong track record may charge higher prices for their products compared to newer or less reputable providers.
Importance of Understanding CRM Software Costs for Businesses
Having a clear understanding of CRM software costs is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about their investment in such systems. By knowing the various expenses involved and the factors that influence pricing, businesses can budget effectively and choose a CRM solution that aligns with their needs and budget constraints.
Factors Affecting CRM Software Costs
When considering the cost of CRM software, various factors come into play that can influence the overall pricing and expenses involved. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about implementing CRM solutions.
Types of CRM Software Deployment
- Cloud-based CRM Software: Cloud-based CRM solutions typically involve subscription-based pricing models, where businesses pay a monthly or annual fee for access to the software. This can be more cost-effective for small to medium-sized businesses as it eliminates the need for upfront hardware costs and reduces IT maintenance expenses.
- On-premise CRM Software: On-premise CRM solutions require businesses to purchase the software upfront and invest in hardware infrastructure to host the system internally. While this may involve higher initial costs, it can be more suitable for larger enterprises with specific security or compliance requirements.
Business Size and CRM Software Pricing
The size of a business can significantly impact the pricing of CRM software. Larger businesses with complex organizational structures and higher user counts may require more advanced CRM features and customization options, leading to higher costs. On the other hand, small businesses with fewer users may opt for more affordable CRM solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Initial Setup Costs
- Licensing Fees: Businesses need to consider the cost of purchasing CRM software licenses for each user.
- Implementation and Customization: Costs associated with setting up and customizing the CRM software to meet the specific requirements of the business.
- Data Migration: Expenses related to transferring existing data into the new CRM system.
Ongoing Maintenance Expenses
- Subscription Fees: Monthly or annual fees for cloud-based CRM software.
- Technical Support: Costs for ongoing technical assistance and software updates.
- Training: Expenses for training employees on how to use the CRM software effectively.
Additional Features and Integrations
Businesses may incur additional costs for integrating CRM software with other tools and systems, as well as for advanced features such as analytics, marketing automation, or AI capabilities. These add-ons can enhance the functionality of the CRM system but may come at an extra cost.
Customization Options and Pricing
The degree of customization required in a CRM software solution can impact pricing. Businesses that need extensive customization to align the software with their unique processes and workflows may face higher costs compared to those opting for out-of-the-box solutions.
Training and Support Services
Investing in training and support services is essential for successful CRM software implementation. Businesses need to budget for training sessions, ongoing support, and consulting services to ensure that employees can effectively utilize the CRM system, which can add to the overall cost of CRM software implementation.
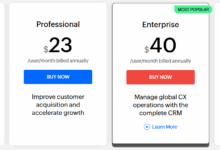
Types of Pricing Models
When it comes to CRM software, there are various pricing models that providers use to offer their services. Understanding these models can help businesses choose the one that best suits their needs and budget.
Subscription-Based vs. One-Time Payment Models
- Subscription-based models: Customers pay a recurring fee at regular intervals (monthly, quarterly, yearly) to access the software. This model often includes updates, maintenance, and support services.
- One-time payment models: Customers make a single payment to purchase the software outright. Additional costs may apply for updates and support.
Usage-Based Pricing vs. Tiered Pricing
- Usage-based pricing: Customers pay based on their usage of the software, such as the number of users or data storage. This can be cost-effective for businesses with fluctuating needs.
- Tiered pricing: Customers select from different tiers of service with varying features and pricing. This allows businesses to choose a package that aligns with their requirements.
Cost Components in Subscription-Based Pricing
- Licensing fees: The cost of using the software.
- Implementation and training: Costs associated with setting up and training users on the software.
- Support and maintenance: Fees for ongoing support and updates.
Freemium Pricing Strategies
Freemium pricing offers a basic version of the software for free, with the option to upgrade to a paid version for additional features. This strategy can attract customers to try the software before committing to a purchase, increasing customer acquisition and retention rates.
Hidden Costs to Consider
When estimating CRM software expenses, businesses often overlook various hidden costs that can significantly impact the total cost of ownership. These hidden costs can arise from customization, integration, training, support, unexpected fees, and the choice between cloud-based or on-premise solutions.
Customization and Integration Impact
Customizing the CRM software to meet specific business requirements and integrating it with existing systems can lead to additional costs. Businesses may need to hire developers or consultants to tailor the software, which can increase the overall expenses.
Training and Support Costs
Training employees to effectively use the CRM software and providing ongoing support can incur additional expenses. Businesses need to invest in training programs and resources to ensure that users are proficient in utilizing the software, which contributes to the total cost of ownership.
Unexpected Fees and Charges
During the implementation of CRM software, unexpected fees or charges may arise, such as data migration costs, additional user licenses, or maintenance fees. These unforeseen expenses can impact the budget and should be considered when estimating CRM software costs.
Long-Term Financial Implications of User Training
Neglecting adequate user training for CRM software can have long-term financial implications. Poor user adoption due to lack of training can result in inefficiencies, errors, and decreased productivity, ultimately affecting the return on investment and increasing the total cost of ownership.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise CRM Systems
The cost differences between cloud-based CRM solutions and on-premise systems should be carefully evaluated. While cloud-based solutions may have lower initial costs and offer scalability, on-premise systems may involve higher upfront investments but lower long-term expenses. Businesses need to assess their specific needs and budget constraints when deciding between the two options.
Cost-Saving Benefits of Automation
Automating certain CRM processes can lead to cost savings over time. While there may be an initial investment required for implementing automation tools, the efficiency gains, improved accuracy, and reduced manual work can contribute to long-term cost savings and increased productivity.
Budgeting for CRM Software
When it comes to implementing CRM software, budgeting is a crucial aspect that businesses need to consider. Creating a budget for CRM software can help organizations allocate resources effectively and ensure a successful implementation. Here are some tips and strategies to help businesses manage CRM software costs:
Creating a Budget for CRM Software Implementation
- Define your goals and requirements: Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with CRM software to determine the features and functionalities you need.
- Research pricing options: Compare different CRM software vendors and pricing models to find a solution that fits your budget and requirements.
- Allocate resources wisely: Set aside a realistic budget for CRM software implementation, considering not just the initial costs but also ongoing expenses.
Aligning CRM Software Costs with Financial Goals
- Ensure ROI alignment: Evaluate how CRM software costs align with your organization’s financial goals and expected returns on investment.
- Focus on value: Prioritize features that provide the most value to your business to make the most of your CRM investment.
- Track expenses: Regularly monitor and track CRM software expenses to stay within budget and adjust as needed.
Negotiating Pricing with CRM Software Vendors
- Request customized quotes: Ask CRM software vendors for personalized pricing based on your specific needs and budget constraints.
- Seek discounts or promotions: Inquire about discounts, special offers, or flexible payment plans to reduce CRM software costs.
- Consider long-term partnerships: Negotiate pricing based on long-term commitments or bundled services to secure better deals.
Conducting a Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Evaluate potential benefits: Assess the expected benefits of CRM software implementation against the associated costs to determine its viability.
- Consider intangible benefits: Factor in qualitative benefits like improved customer satisfaction or enhanced productivity in your analysis.
- Review alternatives: Compare the cost-benefit of CRM software with alternative solutions to make an informed decision.
Hidden Costs and Prioritizing Features
- Account for hidden costs: Be aware of additional expenses such as customization, training, data migration, and ongoing support when budgeting for CRM software.
- Priority-based feature selection: Identify must-have features and functionalities based on your budget constraints to streamline implementation.
- Balance cost and quality: Opt for a CRM solution that offers the right balance of cost-effectiveness and quality to maximize ROI.
Forecasting Long-Term Expenses and Tracking ROI
- Estimate maintenance costs: Anticipate long-term expenses related to CRM software maintenance, upgrades, and scalability to avoid unexpected financial burdens.
- Track key performance indicators: Monitor KPIs such as customer retention rate, lead conversion rate, and customer lifetime value to measure the ROI of your CRM software investment.
- Adjust strategies: Use KPI insights to refine your CRM strategies, optimize processes, and enhance customer relationships for better financial outcomes.
ROI and Cost-Benefit Analysis
Implementing CRM software can be a significant investment for businesses, so it is crucial to understand the return on investment (ROI) and conduct a cost-benefit analysis before making a decision.
Calculating ROI
Calculating the ROI of CRM software involves comparing the benefits gained from the software against the costs incurred. This can be done by measuring the increase in sales, customer retention rates, productivity improvements, and cost savings resulting from using the CRM system.
Importance of Cost-Benefit Analysis
Conducting a cost-benefit analysis helps businesses evaluate whether the benefits of implementing CRM software outweigh the costs involved. It allows companies to make informed decisions based on a comprehensive assessment of both the tangible and intangible benefits of CRM.
Key Metrics for Measuring Effectiveness
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost incurred to acquire a new customer through CRM software.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The total revenue expected from a customer over their entire relationship with the company.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of leads that convert into paying customers with the help of CRM.
- Customer Churn Rate: The rate at which customers stop using the company’s services, which can be reduced with effective CRM strategies.
- Customer Satisfaction Scores: Feedback from customers on their experience with the company, influenced by CRM interactions.
Customization and Scalability
Customization options play a crucial role in the cost of CRM software. Tailoring the software to meet specific business needs can increase initial costs but can also lead to more efficient processes and higher productivity in the long run.
Impact of Customization on CRM Software Costs
- Customizing CRM software to align with unique business processes can involve additional development work, leading to higher upfront costs.
- However, customized CRM solutions can improve user adoption rates and overall efficiency, potentially resulting in long-term cost savings.
- Third-party integrations, data migration, and training for employees on the customized system are additional costs to consider.
Scalability of CRM Software
- Scalability refers to the ability of CRM software to grow and adapt as a business expands or changes.
- Choosing a CRM system that can scale with your business can help avoid the need for a costly migration to a new system down the line.
- Scalable CRM software allows for the addition of new features, users, and data storage capabilities as needed, without major disruptions or expenses.
Costs of Scaling Up vs. Implementing a New CRM System
- Scaling up an existing CRM system usually involves additional licensing fees, hardware upgrades, and customization costs to accommodate the increased user base or data volume.
- Implementing a new CRM system may require upfront investments in software licenses, implementation services, data migration, and employee training.
- Comparatively, scaling up an existing CRM system is often more cost-effective and less disruptive than implementing a new system from scratch.
Integrations and Add-Ons
When considering CRM software, it’s crucial to evaluate the integrations and add-ons available to enhance its functionality and compatibility with existing business systems. Let’s explore the options and strategies for effectively managing these integrations.
Common Integration Options
Before selecting a CRM software, research the compatibility with common business systems such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and project management tools. Some popular integration options include:
- Integration with Email Marketing Platforms (e.g., MailChimp, Constant Contact)
- Integration with Accounting Software (e.g., QuickBooks, Xero)
- Integration with Project Management Tools (e.g., Trello, Asana)
Popular Add-Ons Comparison
Here is a comparison of features and pricing for three popular add-ons that can extend the functionality of CRM software:
| Add-On | Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Email Marketing Integration | Automated email campaigns, lead tracking | $20/month |
| Social Media Integration | Social listening, engagement analytics | $15/month |
| Advanced Reporting | Customized dashboards, forecasting tools | $25/month |
Cost Analysis Table
Here is a cost analysis table showcasing the initial setup costs, ongoing subscription fees, and potential savings or revenue increase from each integration or add-on:
| Integration/Add-On | Initial Setup Cost | Subscription Fee | Potential ROI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Email Marketing Integration | $100 | $20/month | $500/month |
| Social Media Integration | $50 | $15/month | $300/month |
| Advanced Reporting | $200 | $25/month | $700/month |
Implementation Process Management
When managing the implementation of integrations and add-ons, follow these steps to minimize disruptions and optimize performance:
- Evaluate the compatibility and necessity of each integration.
- Create a detailed implementation plan with clear timelines and responsibilities.
- Conduct thorough testing before full deployment.
- Provide training to employees on using the new integrations effectively.
ROI Evaluation Strategy
Develop a strategy for evaluating the ROI of integrating CRM software with various systems and add-ons by tracking key metrics such as:
- Increased lead conversion rates
- Reduced customer acquisition costs
- Enhanced customer retention and satisfaction
Cost-Saving Tips
In today’s competitive business landscape, finding cost-effective solutions is crucial for companies of all sizes. When it comes to adopting CRM software on a budget, there are several strategies that businesses can implement to save costs and maximize their ROI.
Opting for Open-Source CRM Solutions
Open-source CRM solutions can be a cost-effective alternative for businesses looking to save on software expenses. These platforms are often free to use, allowing companies to avoid hefty licensing fees associated with proprietary CRM software. While open-source options may require more customization and technical expertise, the cost savings can be significant in the long run.
Reducing Ongoing Maintenance and Upgrade Costs
To minimize ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs of CRM software, businesses can consider investing in cloud-based solutions. Cloud-based CRM systems typically require lower upfront investment and offer automatic updates, reducing the need for costly manual maintenance. By leveraging cloud technology, companies can ensure their CRM software remains up-to-date without incurring additional expenses.
Implementing Efficient Training Programs
Another cost-saving tip for businesses adopting CRM software is to focus on efficient training programs for employees. By providing comprehensive training and resources, companies can reduce the risk of errors and inefficiencies that may result in additional costs down the line. Investing in proper training can help employees maximize the use of CRM software, leading to improved productivity and cost savings.
Industry-Specific Pricing Considerations
In the realm of CRM software costs, different industries may experience varying pricing structures based on their unique needs and requirements. Understanding how CRM software costs differ across sectors such as healthcare, retail, finance, and more can help businesses make informed decisions when selecting a CRM solution.
Healthcare Industry
- Healthcare CRM software often involves specialized features to manage patient relationships, appointments, and medical records.
- Customization options for HIPAA compliance and data security are crucial in healthcare CRM solutions.
- Providers like Salesforce Health Cloud, Cerner, and Epic offer industry-specific CRM solutions with pricing tailored to the healthcare sector.
Retail Industry
- Retail CRM software focuses on customer engagement, loyalty programs, and inventory management.
- Pricing models for retail CRM may include tiered plans based on the number of customer contacts or transactions.
- Examples of CRM providers for retail include Shopify, Lightspeed, and Vend, each with pricing designed for retail businesses.
Finance Industry
- CRM solutions for the finance sector emphasize relationship management, lead tracking, and regulatory compliance.
- Integration with financial tools and analytics capabilities are key features in CRM software for finance.
- Financial CRM providers such as Microsoft Dynamics 365, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM offer packages tailored to the needs of financial institutions.
Factors such as industry-specific regulations, data security requirements, and integration with sector-specific tools influence CRM software pricing in healthcare, retail, and finance.
Vendor Selection and Negotiation
When it comes to selecting a CRM software vendor, cost considerations play a crucial role in the decision-making process. Finding the right balance between affordability and quality is essential to ensure that your investment yields a positive return. In addition to pricing, negotiating with vendors can also help you secure better deals and contract terms.
Tips for Negotiating Pricing and Contract Terms
- Do your research: Before entering into negotiations, make sure to research the market prices for CRM software and familiarize yourself with common contract terms.
- Highlight your needs: Clearly communicate your specific requirements to the vendor and emphasize the features that are most important to your business.
- Ask for discounts: Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts or special offers, especially if you are purchasing multiple licenses or committing to a long-term contract.
- Flexibility in payment terms: Negotiate flexible payment terms that align with your budget and cash flow requirements.
- Consider value-added services: Inquire about any additional services or support that the vendor can offer as part of the package to enhance the overall value of your investment.
Importance of Evaluating Vendor Reputation and Support Services
While cost is a significant factor in choosing a CRM software vendor, it is equally important to evaluate the vendor’s reputation and support services. Opting for a reputable vendor with a track record of providing excellent customer support can help you mitigate potential issues and ensure a smooth implementation process.
Remember, the cheapest option may not always be the best in the long run if it comes with poor support and service quality.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The total cost of ownership (TCO) in the context of CRM software refers to the complete cost associated with acquiring, implementing, maintaining, and using the CRM system over its entire lifecycle.
Factors Contributing to TCO
- Maintenance: Regular updates, bug fixes, and technical support add to the ongoing costs of a CRM system.
- Upgrades: Costs related to upgrading the software to newer versions or adding new features to meet evolving business needs.
- User Training: Expenses for training employees on how to effectively use the CRM system to maximize its benefits.
TCO Calculation Example
TCO = (Initial Software Cost + Implementation Costs + Training Expenses) + (Maintenance Costs + Upgrade Costs) – (Savings or Benefits from Increased Efficiency)
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario where a company invests $50,000 in CRM software, incurs $20,000 in implementation and training costs, $10,000 annually in maintenance and upgrades, and expects to save $15,000 per year from improved efficiency. The TCO calculation would be as follows:
TCO = ($50,000 + $20,000) + ($10,000) – ($15,000) = $65,000
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
In the realm of CRM software costs, real-world examples and case studies can provide valuable insights into how businesses manage expenses, handle unexpected challenges, and make strategic decisions. Let’s delve into specific scenarios to understand the impact of cost management strategies in different contexts.
Small Business Cost Management Case Study
One small business, a boutique marketing agency, effectively managed CRM software costs within a tight budget by opting for a cloud-based CRM solution with a monthly subscription model. By carefully analyzing their needs and selecting only essential features, they were able to avoid unnecessary expenses. Additionally, the business negotiated a discount for committing to a long-term contract, further reducing costs while ensuring access to critical CRM functionalities.
Medium-Sized Company Unexpected Expenses Example
A medium-sized manufacturing company encountered unexpected CRM software expenses during implementation when they realized the need for extensive data migration and customization to align the system with their unique processes. Despite initial budget constraints, the company prioritized investing in these adaptations to maximize the CRM’s effectiveness. Through strategic planning and reevaluation of priorities, they managed to overcome the financial challenges and successfully implement the CRM solution within an adjusted budget.
Comparison of Cost Management Strategies in the Same Industry
Comparing two businesses in the healthcare sector, one efficiently managed CRM software costs by opting for a scalable solution that allowed gradual expansion and customization based on evolving needs. In contrast, another healthcare provider overspent on CRM software by investing in unnecessary add-ons and failing to assess long-term scalability requirements. The key difference lay in the strategic decision-making process, where the former prioritized flexibility and cost-effectiveness while the latter focused on short-term gains without considering future implications.
Role of Scalability in CRM Cost Management
A growing e-commerce enterprise successfully adapted its CRM system to accommodate expansion without significant cost increases by choosing a modular CRM platform that could scale seamlessly with business growth. This strategic decision allowed the company to add new functionalities and users gradually as needed, aligning costs with revenue generation. The emphasis on scalability not only optimized CRM software expenses but also supported the business’s long-term sustainability.
Impact of Customization on CRM Expenses
In a case study of a tech startup that opted for extensive CRM customization, the initial investment seemed justified to align the system with specific workflows and data requirements. However, over time, the company faced increasing maintenance costs, integration challenges, and compatibility issues with future upgrades. The financial implications of extensive customization highlighted the importance of balancing customization needs with long-term cost considerations to avoid unnecessary expenses in the evolving CRM landscape.
Future Trends in CRM Software Costs
The future of CRM software costs is likely to be influenced by advancements in technology, changing customer expectations, and emerging trends in the industry. Let’s explore some potential developments that could impact the pricing of CRM software in the years to come.
AI Integration in CRM
With the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) in CRM systems, we can expect to see a shift in pricing models. AI-powered features such as predictive analytics, chatbots, and personalized recommendations may become standard offerings, leading to a potential increase in costs. Organizations that leverage AI capabilities to enhance customer engagement and drive sales may need to invest more in CRM software to stay competitive in the market.
Personalized Pricing Models
As businesses focus on delivering personalized experiences to customers, CRM software vendors may introduce more flexible pricing models. Tailored pricing based on the specific needs and usage of each organization could become more common. This trend towards personalized pricing may result in a more cost-effective approach for companies with varying requirements, allowing them to pay for the features and functionalities they actually use.
Evolving Customer Expectations
The changing landscape of customer expectations, driven by factors such as digital transformation and the rise of omnichannel communication, could impact CRM software pricing strategies. Vendors may need to adapt their pricing structures to accommodate the demand for seamless integration across multiple touchpoints and personalized interactions. This shift towards meeting evolving customer needs may influence the development of new pricing tiers or features, potentially affecting overall costs for businesses.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding CRM software costs is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions and maximize their ROI. By considering various factors and implementing cost-saving strategies, companies can effectively manage their CRM expenses and drive growth.